Vacuum Casting begins by producing a master model, typically using Stereolithography or Laser Sintering, with a high-quality surface finish. A silicone mold is then created by casting silicone around the master copy, partially under vacuum to avoid air bubbles. After curing, the silicone mold is cut according to predefined parting planes, and the master is removed, leaving a cavity to make copies.
Type of Casting Technology:

Vacuum Casting

Materials
Vacuum Casting materials can simulate various production materials and properties:
- Rubber: High flexibility
- ABS : High rigidity and strength
- Polypropylene and HDPE: High elasticity
- Polyamide and glass-filled nylon: High rigidity
- Polycarbonate and PMMA : Shock resistance, translucence, high-temperature resistance
- Filled ABS : Fire resistance and retardant

Dimensional Accuracy
±0.3% (with a lower limit of ±0.3 mm on dimensions smaller than 100 mm)

Minimum Wall Thickness
At least 0.75 mm for proper mold filling, with 1.5 mm recommended for best results

Surface Structure
High-quality surface finish comparable to injection molding
Applications of CFD:

Functional parts

Complex ducting

Low-run part production
Up to 20 copies per mold (depending on the mold’s complexity and the casting materials)
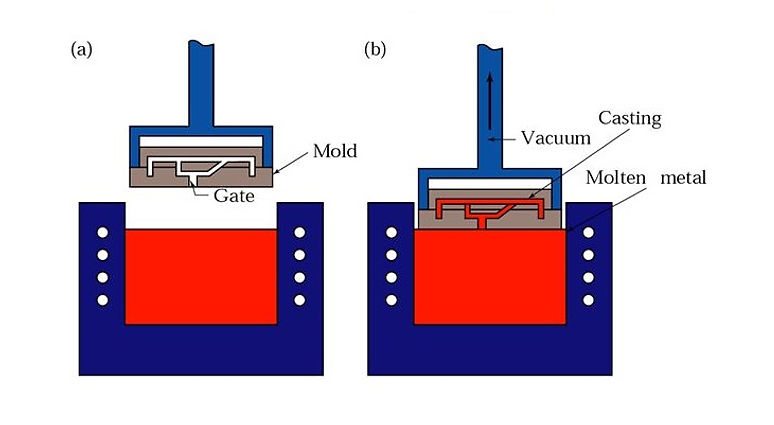
Strengths
1. Functional parts with good mechanical properties
2. Capable of producing complex geometries

Pre-launch product testing

Small series of housings

Concept models

Complex prototypes
Are you looking for complete 3D printing rapid prototyping services? Forcyst is your one-stop solution. Our experts will help you with various prototyping methods, from SLA and SLM to Drop on Demand and SLS, tailored to your requirements.
Forcyst, India’s leading design engineering and rapid prototyping company based in Mumbai, offers comprehensive product design and development solutions. From concept design and research to 3D printing and manufacturing, we serve multiple sectors, including medical, automotive, oil & gas, and more.
